Neuro-Biomechanical Analysis:
Our cutting-edge Neuro Performance Examination is designed to assess, optimize and protect brain health for everyone, including athletes. We focus on evaluating sensory systems, brain processing, and response accuracy, while also emphasizing early detection and prevention of neurological concerns. Through detailed analysis of vision, balance, body awareness, sensory feedback, and cognitive functions, we aim to boost performance and cognition, and proactively address potential neurological challenges.
Services Include:
-
Neurology examination/Assessment: Early detection of potential neurological concerns using advanced diagnostic tools, aimed at preserving brain health and preventing the development of neurodegenerative conditions.
-
Sensory and Cognitive Evaluation: A thorough evaluation focusing on vision, balance, body awareness, sensory feedback, and cognitive function to identify areas for enhancement and risk mitigation.
-
Optimized Neuroperformance Solutions: Tailored, practical treatments and interventions designed to boost your strengths and improve areas of weakness for peak performance. Our goal-oriented approach not only aims at achieving immediate performance goals but also at prolonging your cognitive and physical health through preventative strategies.
-
Benefits for Athletes and Aging Individuals:
-
Enhanced Athletic Performance: Through precise assessments and tailored interventions, athletes can achieve heightened awareness, quicker response times, and improved coordination, contributing to superior performance and reduced risk of injury.
-
Long-term Cognitive and Physical Health: Through proactive assessments, we aim to support not just current performance but also ensure long-term brain health, helping individuals maintain cognitive function and physical abilities as they age.
Why Choose Us?
Our unique method combines comprehensive neurological examinations with the forefront of neuroperformance training and preventative health strategies. This approach sets us apart in our commitment to your long-term health and performance, catering to athletes aiming for excellence in their sports and individuals dedicated to preserving their cognitive and physical well-being through the years.

Neuro-Performance Examination Details
Autonomic Nervous System Performance
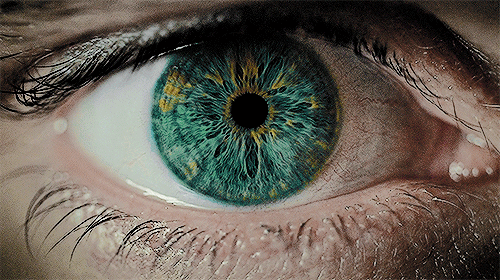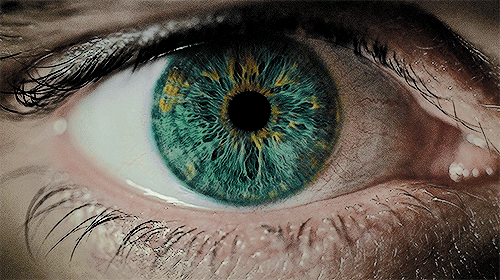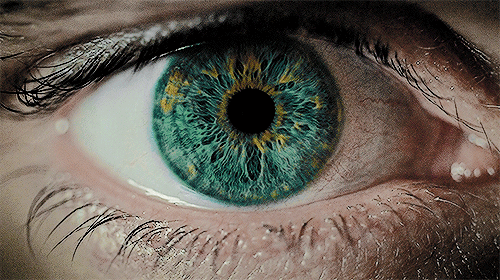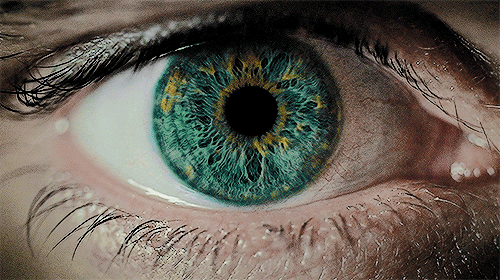
Pupillary Reflex for Enhanced Performance Insights: The pupillary light reflex, a critical measure of the autonomic nervous system's balance between sympathetic (fight or flight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest) responses, serves as a direct indicator of brain state and health, given the eyes' connection to brain tissue. This reflex not only assesses neuro-integrity and autonomic function but also provides objective biomarkers for tailoring therapy dosages and evaluating responses to treatments. It's a powerful tool for understanding how to maintain composure under stress, offering a foundation for performance optimization.
Brain Function Performance

Brain Functionality and Performance Assessment:
Our evaluations delve into the functionality of key brain regions and networks, providing essential insights into your physical and mental performance. Understanding the efficiency, endurance, and functionality of your brain is pivotal for success in both athletic pursuits and cognitive tasks within professional environments. We focus on assessing:
-
Frontal Cortex: Decision-making, problem-solving, and planning.
-
Parietal Lobe: Spatial orientation and perception.
-
Temporal Lobe: Memory and understanding language.
-
Occipital Lobe: Visual processing.
-
Cerebellum: Coordination and precision.
-
Basal Ganglia: Movement regulation and habit formation.
-
Cranial Nerves: Sensory and motor functions.
-
Brainstem Regions: Basic life functions.
-
Brain Networks: Connectivity for complex processing.
-
Autonomic Nervous System: Regulating involuntary bodily functions.
Balance Performance

Balance & Rehabilitation Services Overview:
Our approach to balance integrates the coordination of vision, proprioception, and the vestibular system for optimal stability, crucial in physical activities, post-surgical rehabilitation, and recovery from neurological injuries. Our services include:
-
Balance Screening: Evaluating balance against standard norms.
-
Vestibular Assessments: Diagnosing and treating vestibular system disorders.
-
Neuro-Optometric Rehab: Rehabilitation to improve vision and balance post-surgery.
-
Weight Distribution Correction: Addressing and correcting uneven weight distribution.
-
Balance Management for Neuropathy: Solutions for neuropathy-induced balance issues.
-
TBI Recovery: Specialized programs for balance restoration after traumatic brain injuries.
-
Neuromuscular Re-education: Training for enhanced balance and coordination.
-
Orthopedic Consultation: Assessments for post-injury recovery.
-
Fall Risk Evaluation: Identifying fall risks and implementing preventative strategies.
Sensory Systems Performance

Sensory Motor Integration Simplified: Sensory-motor integration involves the process of the sensory system gathering information, the brain interpreting it, and the muscles responding accordingly. This measurable interaction enhances various aspects of visual and motor skills, including:
-
Visual Clarity and Contrast Sensitivity
-
Depth Perception and Near-Far Quickness
-
Perception Span and Multiple Object Tracking
-
Reaction Time, including Simple and Choice Reaction Times
-
Target Capture and Eye-Hand Coordination
-
Go/No Go Training and Processing Speed
-
Dynamic Visual Focus and Smooth Visual Pursuit
-
Binocular Vision and Visual Concentration
FDA-Cleared Vision Performance Testing

Dynamic Vision, Sports Vision, & Reading Assessments:
Our assessments delve into the brain's control of eye movements to enhance understanding of cognitive function, going beyond simple visual clarity. This insight allows us to create customized interventions to boost performance in daily activities, sports, and reading. We address:
-
Issues with visual focus and concentration
-
Reading difficulties, such as skipping lines or poor comprehension
-
Short attention spans and delayed task completion
-
Coordination, balance, and sports performance challenges
-
Effects of brain trauma on visual processing
-
Reduced reading interest and frequent headaches
Our focused evaluations pinpoint the root causes, laying the groundwork for solutions that enhance reading efficiency, athletic abilities, and overall daily life functioning.
Sports Vision EyeQ Reading EyeQ
Movement Performance

First, MOVE WELL, then MOVE OFTEN.
By evaluating basic movement standards, we can prevent bad habits, fix movement problems, and ensure consistent movement quality. We take into account both neurological and orthopedic aspects to identify which areas need improvement. Our goal is to:
-
Screen for overall movement health,
-
Assess movement function,
-
Measure movement ability,
-
Enhance movement complexity.
This approach helps you move effectively, train proficiently, and develop skills on a solid foundation, steering clear of building fitness on a dysfunctional base.